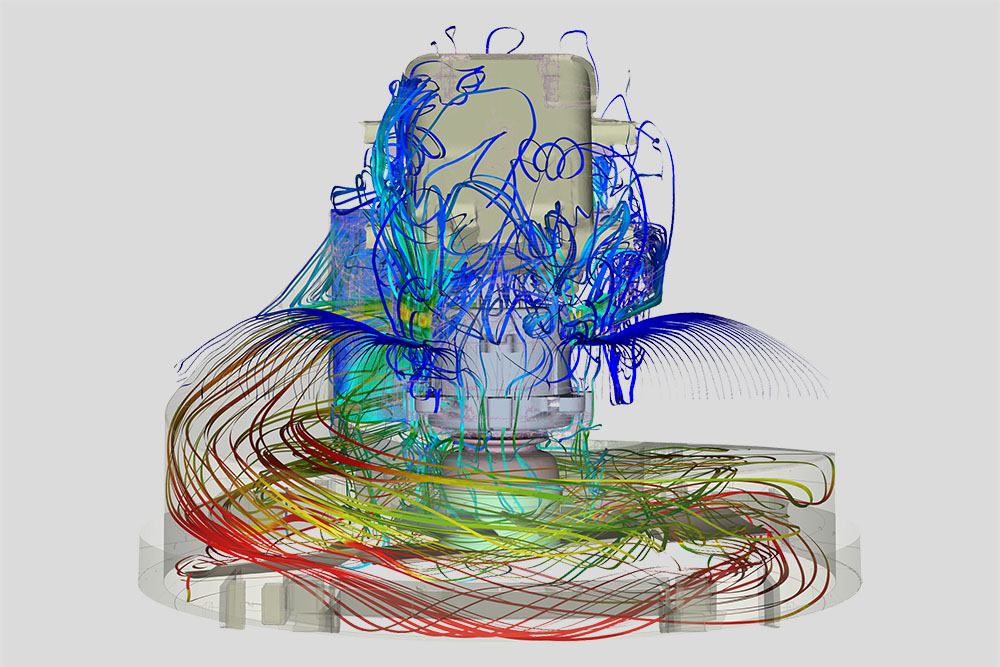
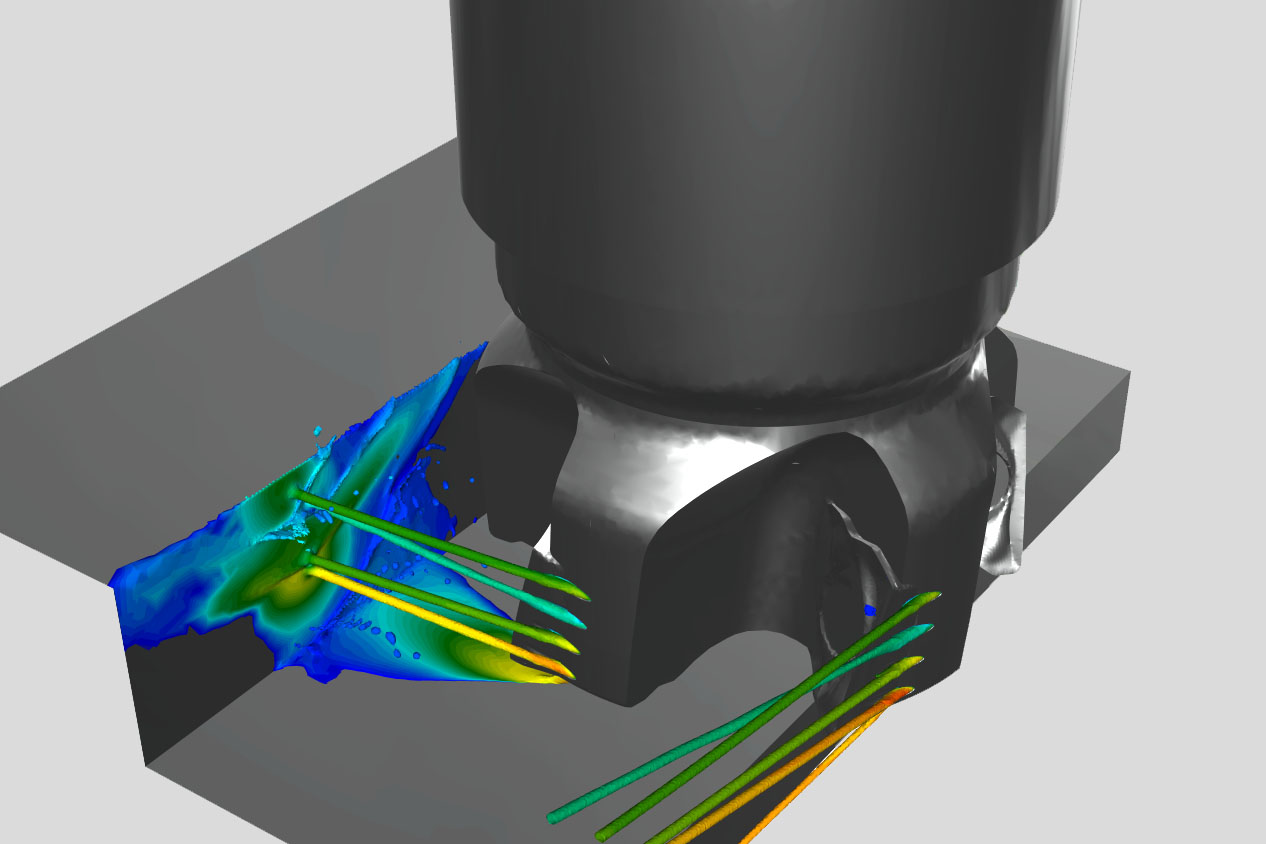
Our expertise
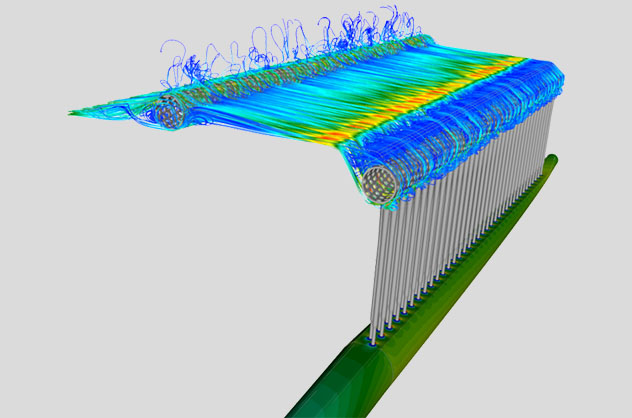
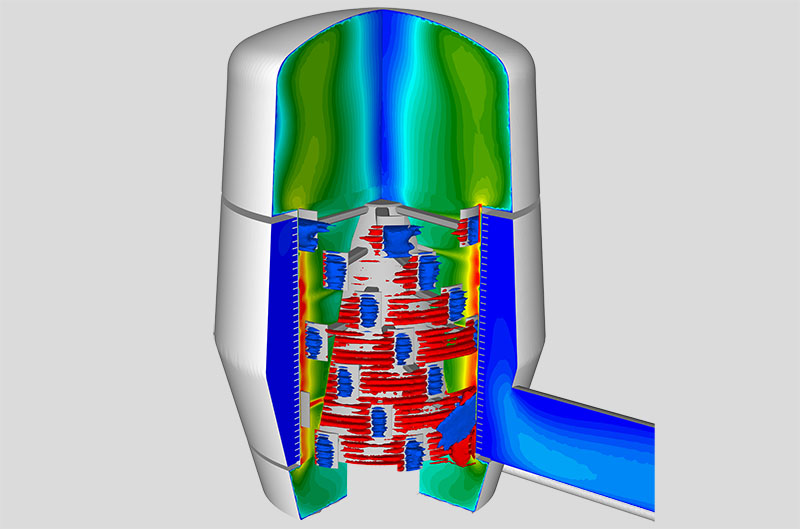
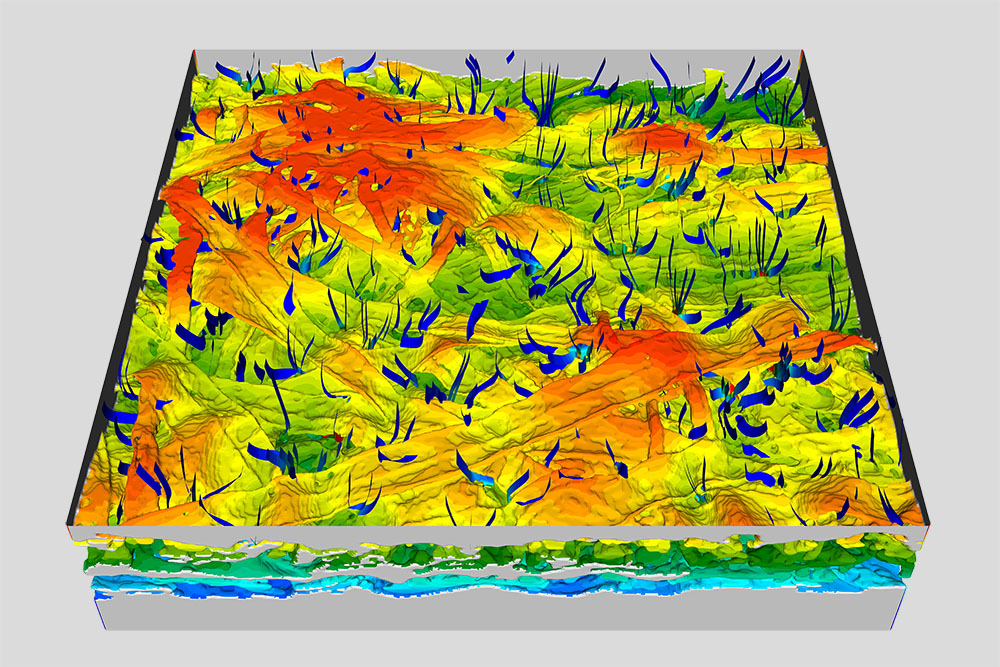
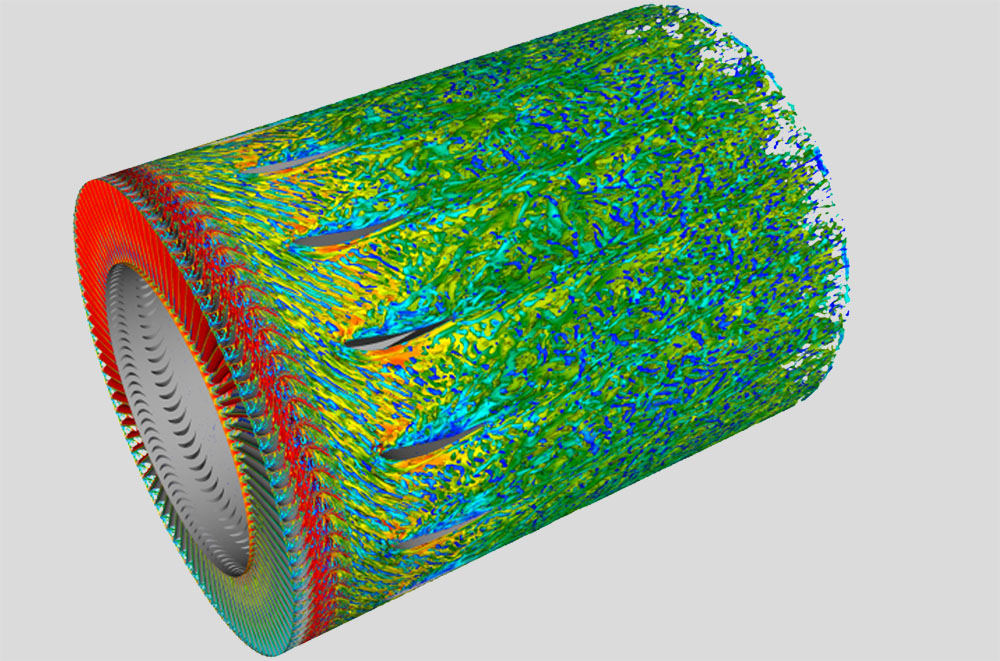
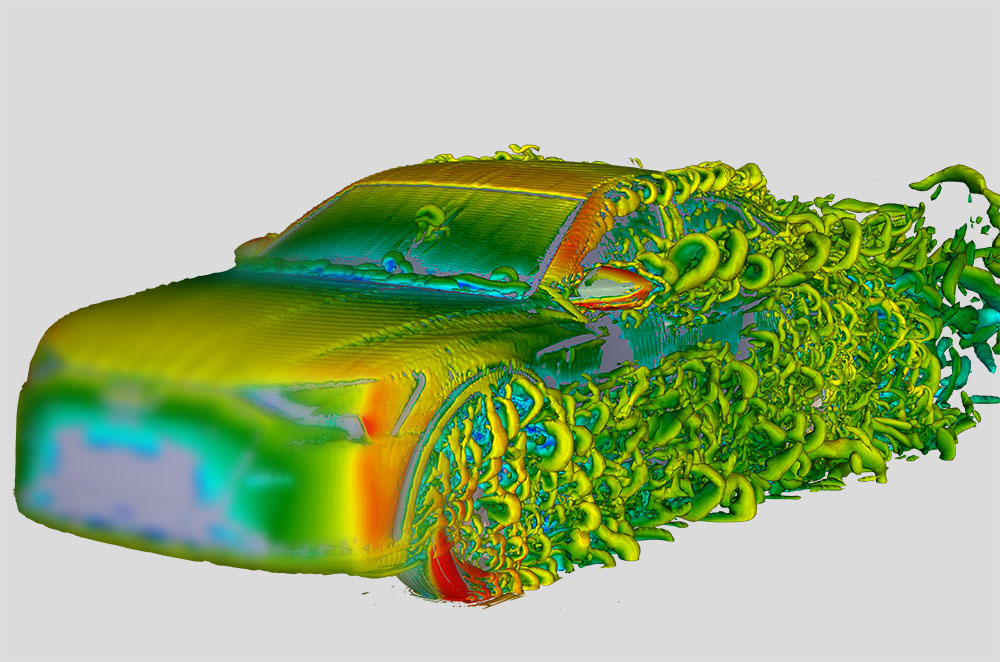
Advanced CFD simulations and analyses build the foundation for the development of individual Riblet solutions and research in this field, and further represent our second major product offering. Based on our profound knowledge, experience and our large computational resources, we provide general CFD calculations and solutions for your flow and heat transfer problems and have additional specializations in Pulp & Paper, Acoustics and Micro- & Nanofluidic.
Pulp & Paper
Enhanced troubleshooting for paper and board machines
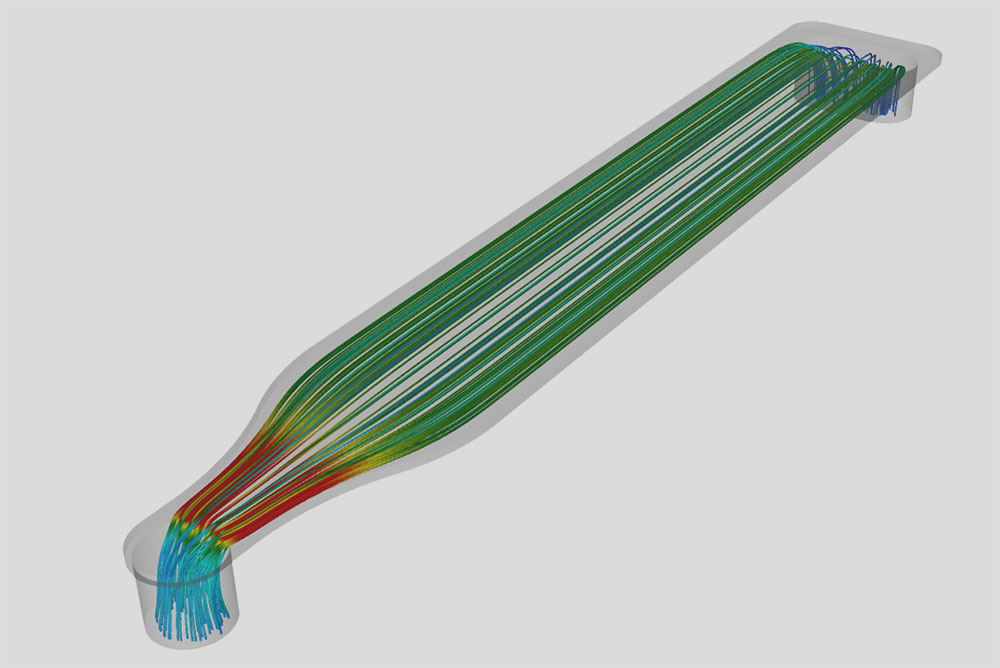
Production processes within the pulp & paper industry are complex and offer a large potential for optimizations. Considering the size of the industry or the worldwide consumption of paper, the impacts of possible process improvements and efficiency increases in an economical and in an ecological sense become apparent. Focusing on the complex process of papermaking, respectively on the different stages of paper machines, CFD simulations are effective and efficient tools for problem solving and process optimizations which can bring significant competitive advantages.
01
Increase Efficiency
02
Detect Problem Sources
Let's talk about how we can help you stand out.
More Information
Acoustics
Identify noise emitters and turn down your acoustic problem
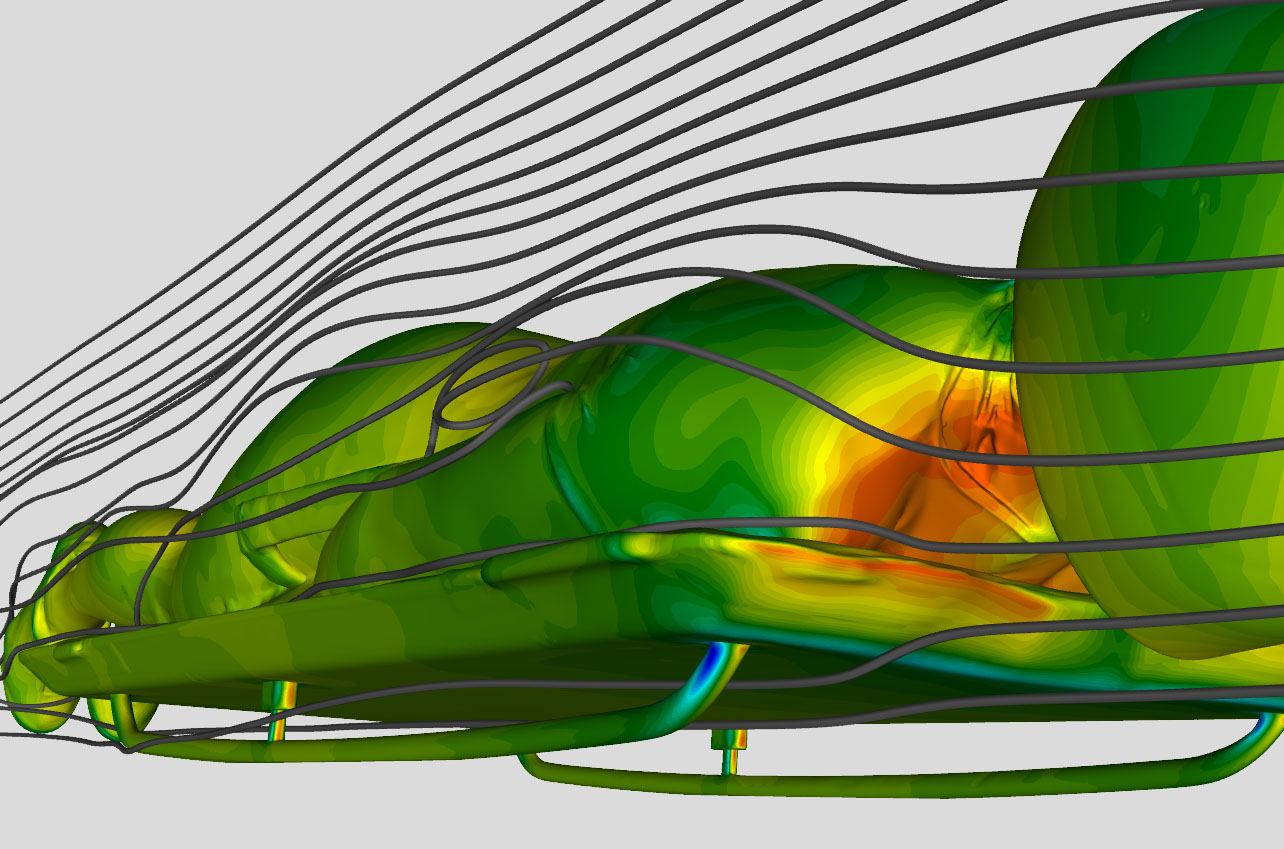
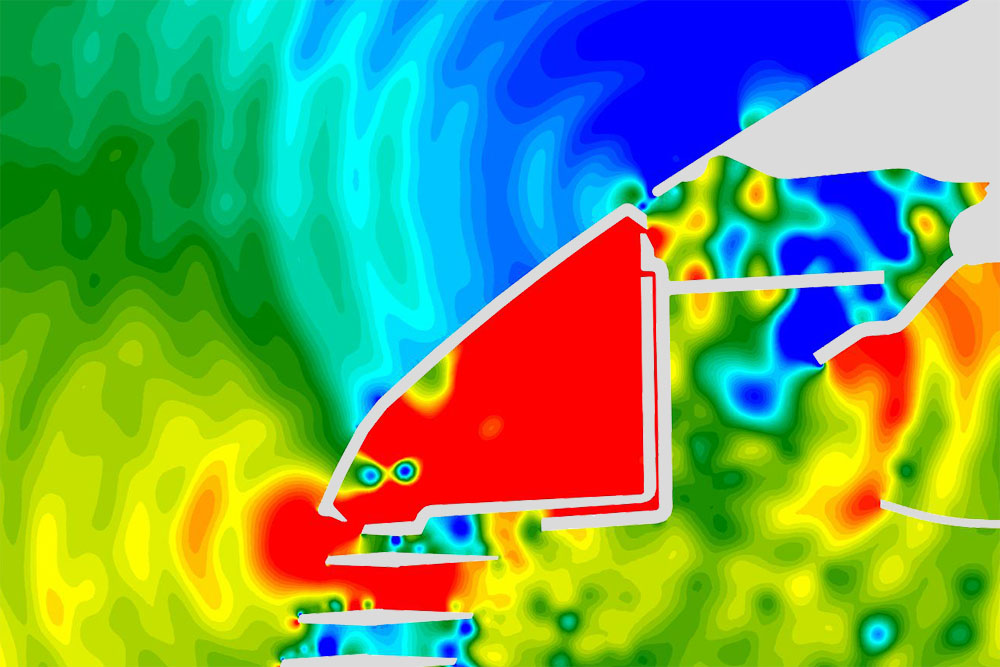
Numerical simulations are essential tools in the field of acoustics and provide solutions for the calculation of sound generation, its propagation and therefore the optimization or even prevention of noise emissions. Two fundamental disciplines of acoustics, which characterize the nature of noise generation, are aeroacoustics and vibro-acoustics. While aeroacoustics regard noise which is caused by turbulent flows or aerodynamic forces in surface interaction, vibro-acoustics comprises noise caused by structural vibrations. The numerical simulation is conducted with a conventional CFD approach complemented by FEM (Finite Element Method) and resulting in sound pressure levels and frequencies at a defined receptor position.
01
Identify Noise Sources
02
Acoustical Optimizations
The application of CFD simulations for acoustic problems is sparse due to their complexity, although a high relevance is given in almost all industrial fields. Exemplary applications with growing and already significant importance of acoustic design are vehicles, wind turbines, turbomachines or rotating components in general. Possessing the necessary experience and knowhow, we provide you with acoustic simulations regardless of your specific setting. Being a leading force of Riblet engineering, which is an effective way to optimize acoustic conditions, we further provide a comprehensive solution including its implementation.
Let's talk about how we can help you stand out.
Contact us
MICROFLUIDICS
Revolutionize biosensor technology by simulating on a micro- & nano-scale
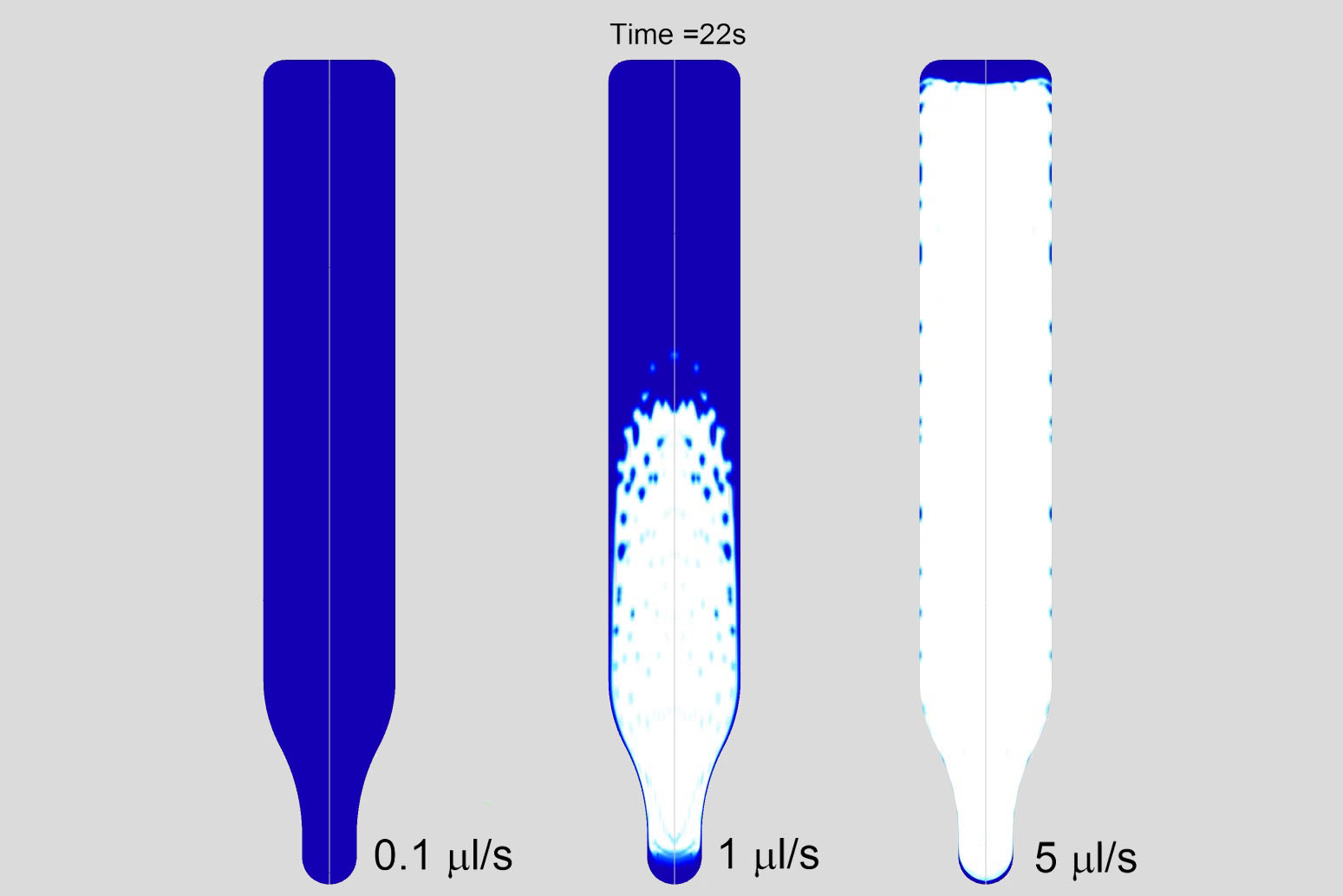
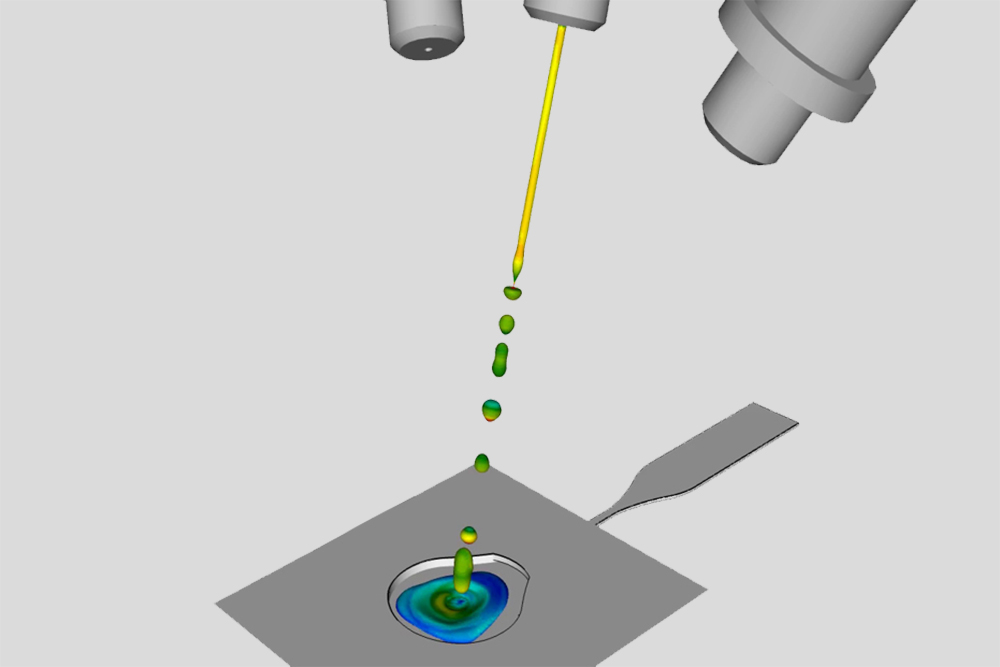
Microfluidics describe the behavior of fluids at a very small scale at which surface forces like capillarity and intermolecular forces dominate volumetric forces. It represents a field with an enormous potential and prospective relevance. While some applications can already be found in industrial use, the topic is still a matter of intense research and product development. Possible applications regard molecular diagnostics, lab-on-a-chip solutions, food industry, pharmaceutical testing and biosensor technology in general. The precise control of small scale fluid flows creates completely new possibilities for developments in such fields. In this sense, especially CFD simulations gain importance by enabling the numerical modeling of viscosity effects, surface tension or advection and diffusion effects. Hereby, the need for costly experiments and time consuming trial & error loops can be overcome.
01
Enable Precise Micro Fluxes
02
Overcome Expensive Trial & Error Loops
Strongly connected to research and participating in respective innovation hubs and ecosystems e.g. Microfluidics Innovation Hub, we offer cutting edge solutions for your application. With our network of industry leading partners we guarantee a comprehensive view on your problem.
Let's talk about how we can help you stand out.
Contact us
CFD Applications
Level up your product and your process by advancedCFD Modeling
Advanced CFD simulations are demanded across all industries and bring significant competitive advantages. In the development stage, numerical modeling prevents costly experiments by enabling realistic virtual prototyping. Existing facilities and processes can be optimized in regard of their energy efficiency or performance. Furthermore, CFD analyses offer efficient and quick possibilities for solving operational problems, resulting in reduced operating costs, enhanced production quality or reduced maintenance efforts and thereby fewer costly facility shutdowns.
01
Accelerate Product Development
02
Improve Process Quality
Beyond our areas of specialization, we provide advanced numerical calculations regarding heat transfer and fluid flow processes of any kind. Thermodynamic and chemical effects are involved in the computational procedure to attain most realistic simulation results. This allows to properly simulate combustion processes and further enables the reduction of exhaust gas emissions or the decrease of technical risks of complex systems. Modeling general particle separation or blending processes, heat exchangers, and filter systems belong to our expertise as well as the simulation of complex multiphase flow conditions and many others.
Let's talk about how we can help you stand out.
Contact us